Bluetooth serial console
Often being caught in situations when I need serial console to Cisco equipment and I don't have one, despite caring several capable linux machines in my pockets, made me do something about it.
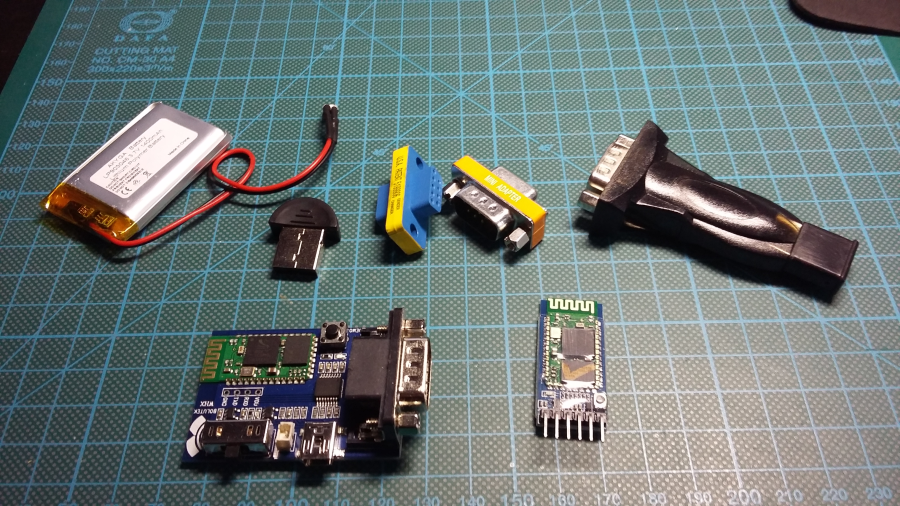
For the experiments, I've got several things:
- DB9 RS232 Bluetooth Serial Adapter (~7-8$)
- HC-05 Bluetooth RF RS232 TTL Module (~3$)
- DB9 M-F Mini Null Modem adapter (~2$)
- DB9 F-F Gender Changer (<1$)
- USB to RS232 Serial DB9 Adapter (~1-4$)
- USB Bluetooth Adapter (~1$)
- 3.7V 1400 mAh Li-Po battery (~7-8$)
- Cisco Blue Console Cable DB9 To RJ45 (~2$)
"DB9" above is actually "DE-9", but "DB9" is used more often.
Install some serial terminal software on the PC (minicom, picocom, nanocom, screen, putty, etc..) - I am going to use picocom.
$ sudo apt-get install -y picocom
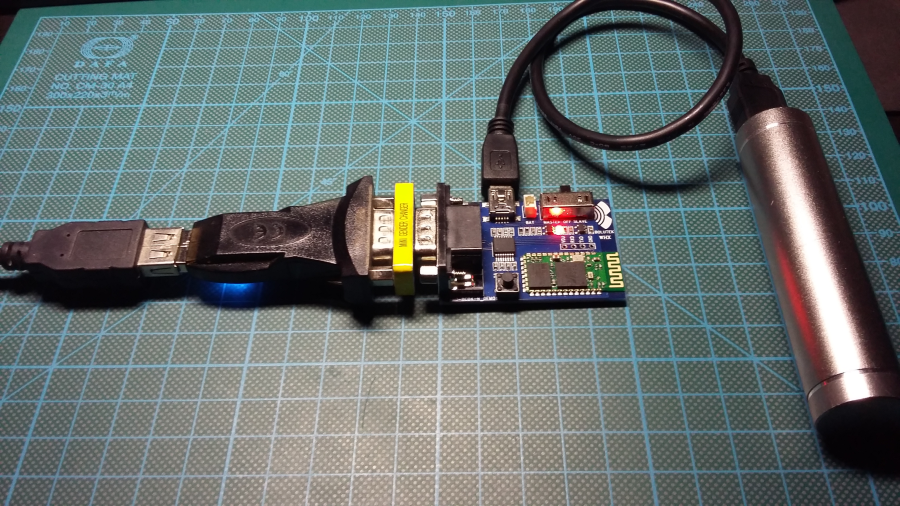
Connect DB9 RS232 Bluetooth adapter via DB9 F-F gender changer to USB Serial adapter. Power the BT board via mini USB cable. Connect USB serial to PC USB port:
Launch serial terminal on it:
$ dmesg | tail | grep tty
[4505336.859339] usb 3-8.1: FTDI USB Serial Device converter now attached to ttyUSB0
$ picocom -c -b 9600 /dev/ttyUSB0
...
Terminal ready
Turn the switch into slave mode. It will respond to serial. Execute 'AT' command, and get the response:
*** BOLUTEK SPP Bluetooth Module V2.44 Init OK in SLAVE mode!***
*** Please input AT+HELP <cr><lf> to get commands list. ***
*** For more information, please visit http://www.bolutek.cn ***
+READY
+PAIRABLE
AT
OK
So, if we connect to the module directly via serial, we are talking to BC04-B BT transceiver part. The list of AT commands is available, but you can get the list directly from the module by issuing 'AT+HELP' :
AT+HELP
Command Description
-----------------------------------------------------------------
AT Check if the command terminal work normally
AT+RESET Software reboot
AT+VERSION Get firmware, bluetooth, HCI and LMP version
AT+HELP List all the commands
AT+NAME Get/Set local device name
AT+PIN Get/Set pin code for pairing
AT+BAUD Get/Set baud rate
AT+CLEAR Remove the remembered remote address
AT+LADDR Get local bluetooth address
AT+RNAME Get remote device name
AT+DEFAULT Restore factory default
AT+CMODE Get/Set connection mode
AT+BIND Get/Set bind bluetooth address
AT+COD Get/Set local class of device
AT+IAC Get/Set inquiry access code
AT+ROLE Get/Set master or slave mode
AT+STATE Get current state
AT+SENM Get/Set security and encryption mode
AT+IPSCAN Get/Set page and inquiry scan parameters
AT+SNIFF Get/Set sniff power table parameters
AT+LOWPOWER Start/Stop low power mode
AT+UARTMODE Get/Set uart stop bits and parity
AT+ENABLEIND Enable/Disable Indication print
AT+LSP List Paired Device List
AT+RESETPDL Reset Paired Device List
AT+REMOVEPDL Remove one entry from Paired Device List
AT+SUPERVISION Get/Set supervision timeout
AT+AUTOINQ Start/Stop auto inquiry
AT+INQ Start inquiry
AT+INQC Cancel ongoing inquiry
(M)AT+AUTOCONN Start/Stop auto connection
(M)AT+INQM Get/Set inquiry parameters
(M)AT+CONNECT Connect to a remote device by BD address
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Note: (M) = The command support master mode only, other commands
support both master and slave mode.
For more information, please visit http://www.bolutek.cn
Copyright@2012 www.bolutek.cn. All rights reserved.
For now, there are only 2 commands relevant to our needs - here we are changing module BT name from default 'BOLUTEK' to 'BTSC' and pin from default '1234' to max. length '0123456789ABCDEF'. Unfortunately it will not let us change BT MAC address via AT commands.
AT+NAME
+NAME=BOLUTEK
AT+NAMEBTSC
+NAME=BTSC
AT+PIN
+PIN=1234
AT+PIN0123456789ABCDEF
+PIN=0123456789ABCDEF
OK
Now we are ready to go.
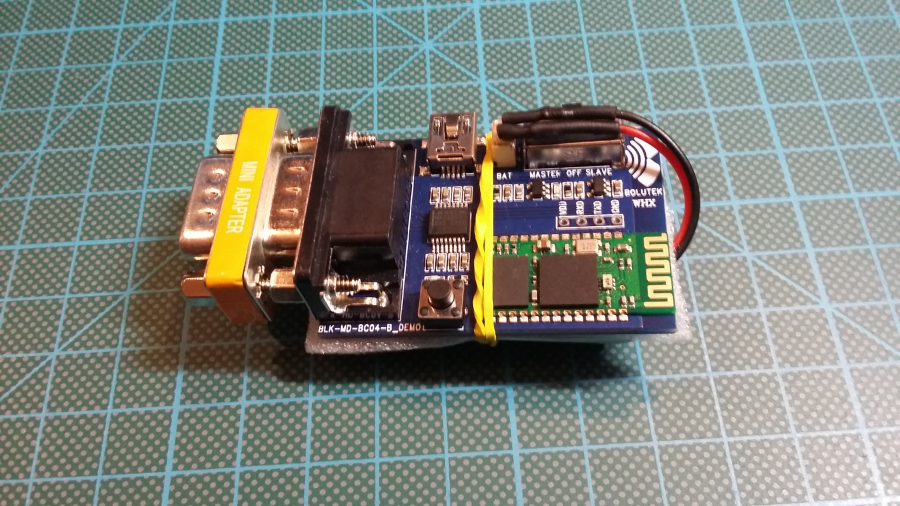
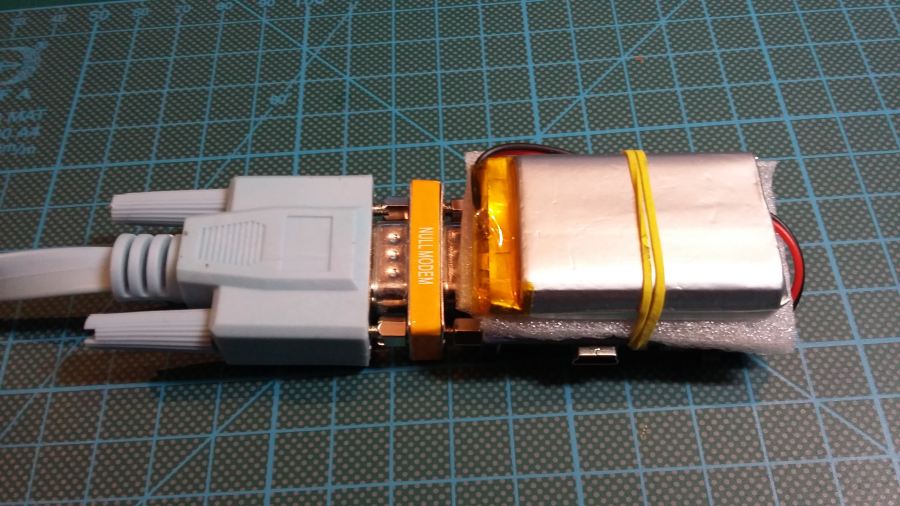
Reassemble the gear: disconnect USB Serial and DB9 gender changer. Connect Null-Modem adapter, blue Cisco cable and Battery.
IMPORTANT: You need Null-Modem adapter for normal use.
Connect Cisco console cable into some Cisco equipment.
Plug USB BT dongle into PC. Dmesg shows:
[4562811.896635] usb 3-8.1: new full-speed USB device number 127 using xhci_hcd
[4562812.002374] usb 3-8.1: New USB device found, idVendor=0a12, idProduct=0001
[4562812.002376] usb 3-8.1: New USB device strings: Mfr=0, Product=2, SerialNumber=0
[4562812.002377] usb 3-8.1: Product: CSR8510 A10
lsusb detects it as:
Bus 003 Device 127: ID 0a12:0001 Cambridge Silicon Radio, Ltd Bluetooth Dongle (HCI mode)
Install bluetooth support:
$ sudo apt-get install bluetooth
Set dongle address to 00:11:22:33:44:55 if manufacturer supports it:
~$ sudo bccmd -d hci0 psset -s 0 bdaddr 0x33 0x00 0x55 0x44 0x22 0x00 0x11 0x00
Or by an easy tool:
$ cd /tmp
$ wget -U "Mozilla" -O bdaddr.tar.bz2 http://www.petrilopia.net/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/bdaddrtar.bz2
$ tar -xvf bdaddr.tar.bz2
$ cd bdaddr/
$ sudo apt-get install libbluetooth-dev
$ make
$ sudo ./bdaddr 00:11:22:33:44:55
Manufacturer: Cambridge Silicon Radio (10)
Device address: 00:11:22:33:44:00
New BD address: 00:11:22:33:44:55
Address changed - Reset device now
After reinserting you can see it with a new address:
$ hcitool dev
Devices:
hci0 00:11:22:33:44:55
$ hciconfig
hci0: Type: BR/EDR Bus: USB
BD Address: 00:11:22:33:44:55 ACL MTU: 310:10 SCO MTU: 64:8
UP RUNNING PSCAN
RX bytes:612 acl:0 sco:0 events:37 errors:0
TX bytes:942 acl:0 sco:0 commands:37 errors:0
Scan for other BT devices and see our Serial module:
$ hcitool scan
Scanning ...
00:10:20:30:40:50 BTSC
List services:
$ sdptool records 00:10:20:30:40:50
Service Name: SPP Dev
Service RecHandle: 0x10000
Service Class ID List:
"Serial Port" (0x1101)
Protocol Descriptor List:
"L2CAP" (0x0100)
"RFCOMM" (0x0003)
Channel: 1
Language Base Attr List:
code_ISO639: 0x656e
encoding: 0x6a
base_offset: 0x100
Connect serial device (funny, you don't need any PIN for that):
$ sudo rfcomm connect hci0 00:10:20:30:40:50
Connected /dev/rfcomm0 to 00:10:20:30:40:50 on channel 1
Press CTRL-C for hangup
Launch serial terminal in another terminal session:
$ sudo picocom /dev/rfcomm0
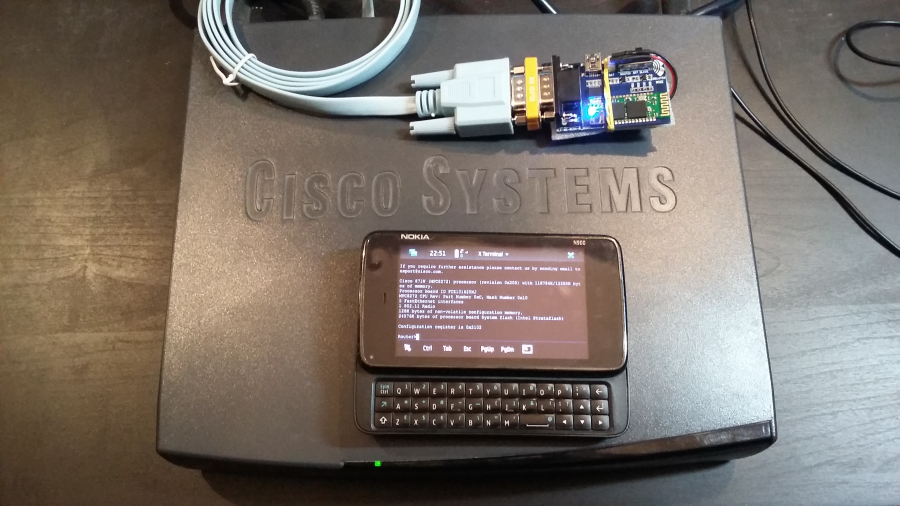
Press 'Enter' - and vuala - you are in Cisco console now:
Terminal ready
Router>
Bluetooth serial adapter module schematics can be found here.
From the module schematics mentioned above we can see it also has LN2054 battery charger, meaning you can go autonomous with the Li-Po battery, and charge it via Mini-USB when possible.
So, after we tested everything with a PC, it's time to do it on a mobile device, like Nokia N900. I did it in a two steps: first, paired bluetooth devices via Maemo GUI (whih is actually not necessary in our case), then edited
/etc/bluetooth/rfcomm.conf file, so it contains:
rfcomm0 {
bind yes;
device 00:10:20:30:40:50;
channel 1;
comment "BTSC";
}
Now, after you enable bluetooth via Maemo GUI, open a terminal, and issue:
Nokia-N900:~# rfcomm connect /dev/rfcomm0
Connected /dev/rfcomm0 to 00:10:20:30:40:50 on channel 1
Press CTRL-C for hangup
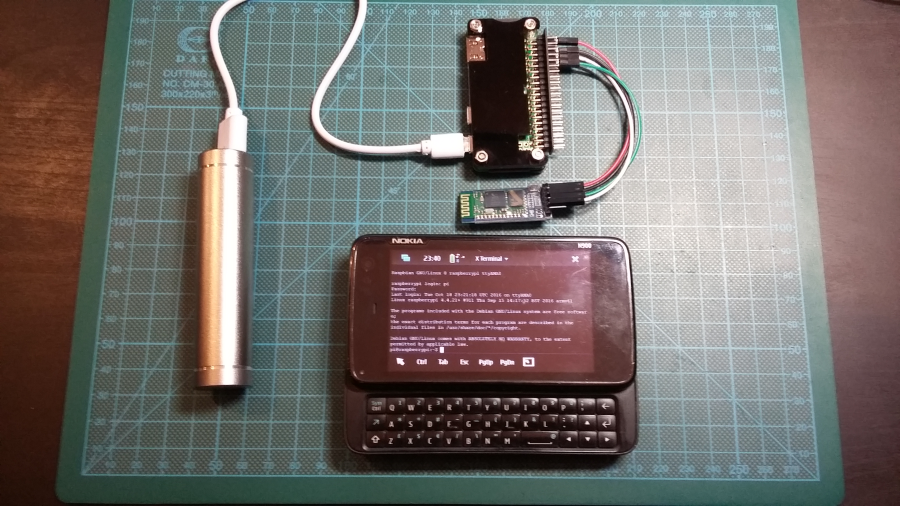
Microcom is a part of the busybox-power (note: Ctrl-X to exit):
Nokia-N900:~# microcom -s 9600 /dev/rfcomm0
Router>
BONUS: talking to Raspberry Pi Zero serial console from Nokia N900 via HC-05 Bluetooth RF RS232 TTL Module :